What Is Embryo Freezing?
How it works, why it works, and why it’s useful for donor egg IVF
Embryo freezing is a process that saves and stores embryos so patients can use them to try for a pregnancy later on. At SIMPLIFY and our partner clinic Pacific Northwest Fertility (PNWF), we freeze the majority of the embryos we develop, whether from a patient’s own eggs, frozen donor eggs, or fresh donor eggs. This guide will take you through the embryo freezing process, from reasons why to success rates.
How Does Embryo Freezing Work?
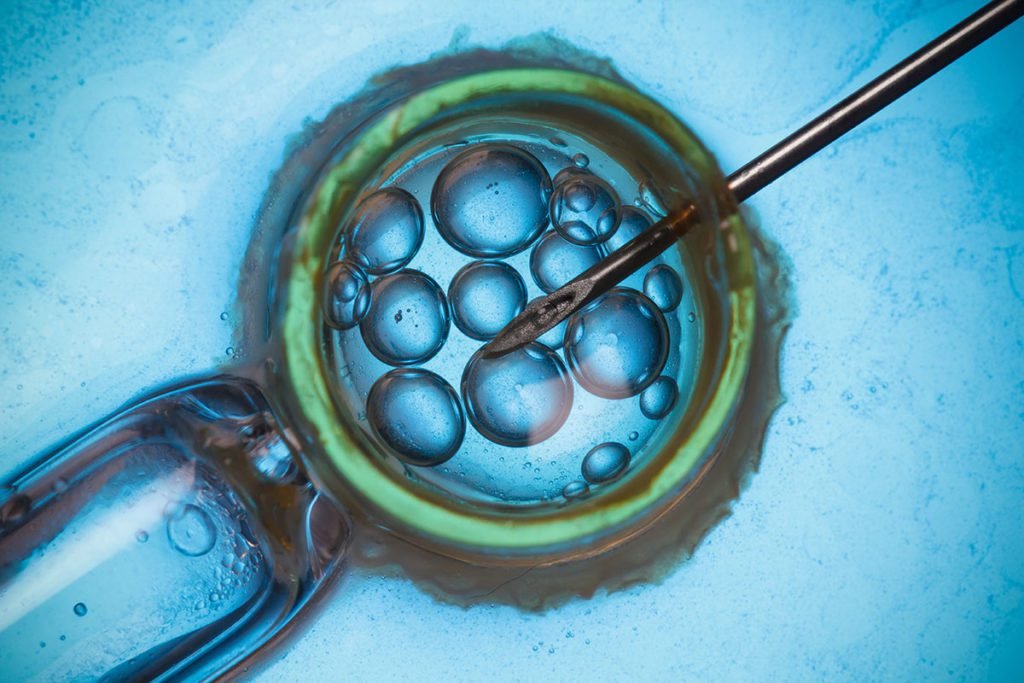
Embryo freezing is an optional step along the in vitro fertilization (IVF) process. It happens after developing embryos in a lab, but before transferring the embryos to a patient’s uterus.
In order to develop the embryos, patients either go through ovarian stimulation and an egg retrieval themselves, or select donor eggs. The eggs are fertilized in a lab with sperm from either the intended parent or a donor. Over the next few days, the fertilized eggs develop into embryos. An embryologist evaluates these embryos and freezes them with a process called vitrification. Vitrification, or “flash-freezing,” freezes the embryos nearly instantly, preserving their structure for later use.
When the patient is ready to try to conceive, one or more of the embryos are thawed and transferred to their uterus, where they hopefully implant and develop into a pregnancy. Frozen embryos can be safely stored for years.
Why Freeze Embryos?
Patients freeze their embryos for many different reasons, including:
Timing: Freezing embryos allows for more flexibility around scheduling the embryo transfer. Especially when using donor eggs, freezing embryos means the egg retrieval, fertilization, and embryo transfer are not all tied together timing-wise, which lowers the risk of needing to cancel or reschedule cycles if one process has unexpected delays.
Genetic Testing: Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT-A) involves taking a small sample from the fresh embryos for evaluation. The embryos are then frozen, as the test results typically take 10-14 days to process.
For Future Use: IVF often results in the development of multiple embryos. As many patients need more than one IVF cycle to become pregnant, they often freeze any additional embryos to use in future cycles. This streamlines the IVF process and lowers overall costs.
For patients using donor eggs, developing and freezing additional embryos is also useful if you wish to try for genetically related siblings in the future, as there is no guarantee that eggs from the same donor will be available years later.
Fertility Preservation: Patients may choose to freeze either eggs or embryos before undergoing chemotherapy, gender-affirming therapy, or other medical treatment that could affect their fertility.
Is Embryo Freezing Expensive?
The majority of embryo freezing costs come from the basic costs of IVF (ovarian stimulation, egg retrieval, fertilization, and more). Freezing embryos adds a few additional expenses, including the freezing and thawing processes and storage costs. However, the cost is a fraction of having to do a second oocyte retrieval. Please contact us to learn more about costs, insurance coverage, and your personal situation.
What Are Frozen Embryo Transfer Success Rates?
IVF and cryopreservation (freezing) technologies have come a very long way over the past few decades. Today, success rates are very similar for fresh vs. frozen embryos. Our embryologists at PNWF have led the field of egg and embryo freezing, thawing, and transfer, and we have some of the highest success rates in the world. Freezing your embryos is a safe and proven process that can give you more flexibility and peace of mind during your donor egg IVF journey. For more information, reach out to us today.